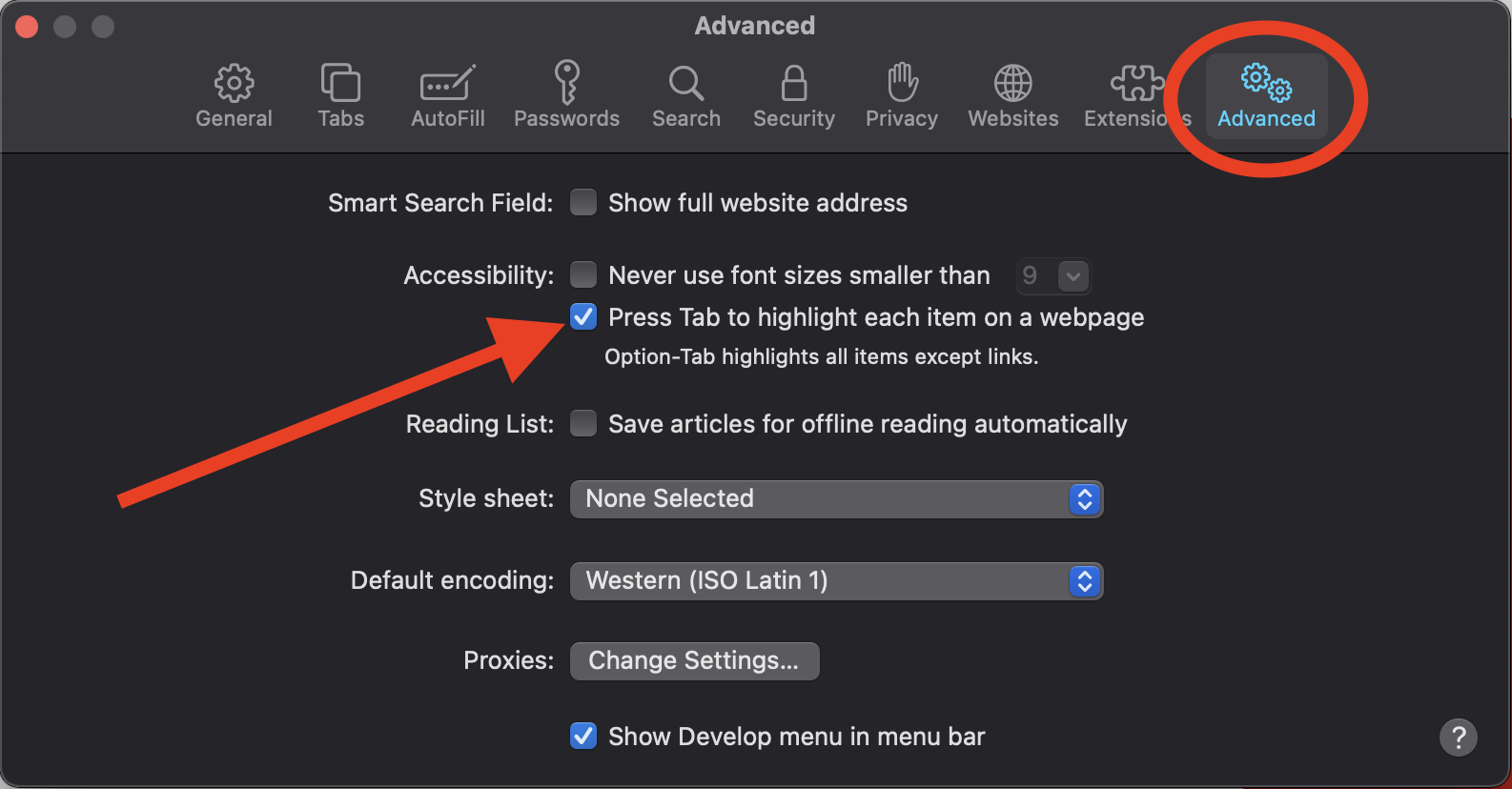
Mac OS User Tabbing
For Mac OS users, there is a system setting that may not allow you to tab onto several types of elements in a web page. To change this setting:
Open System Preferences and go to Keyboard:
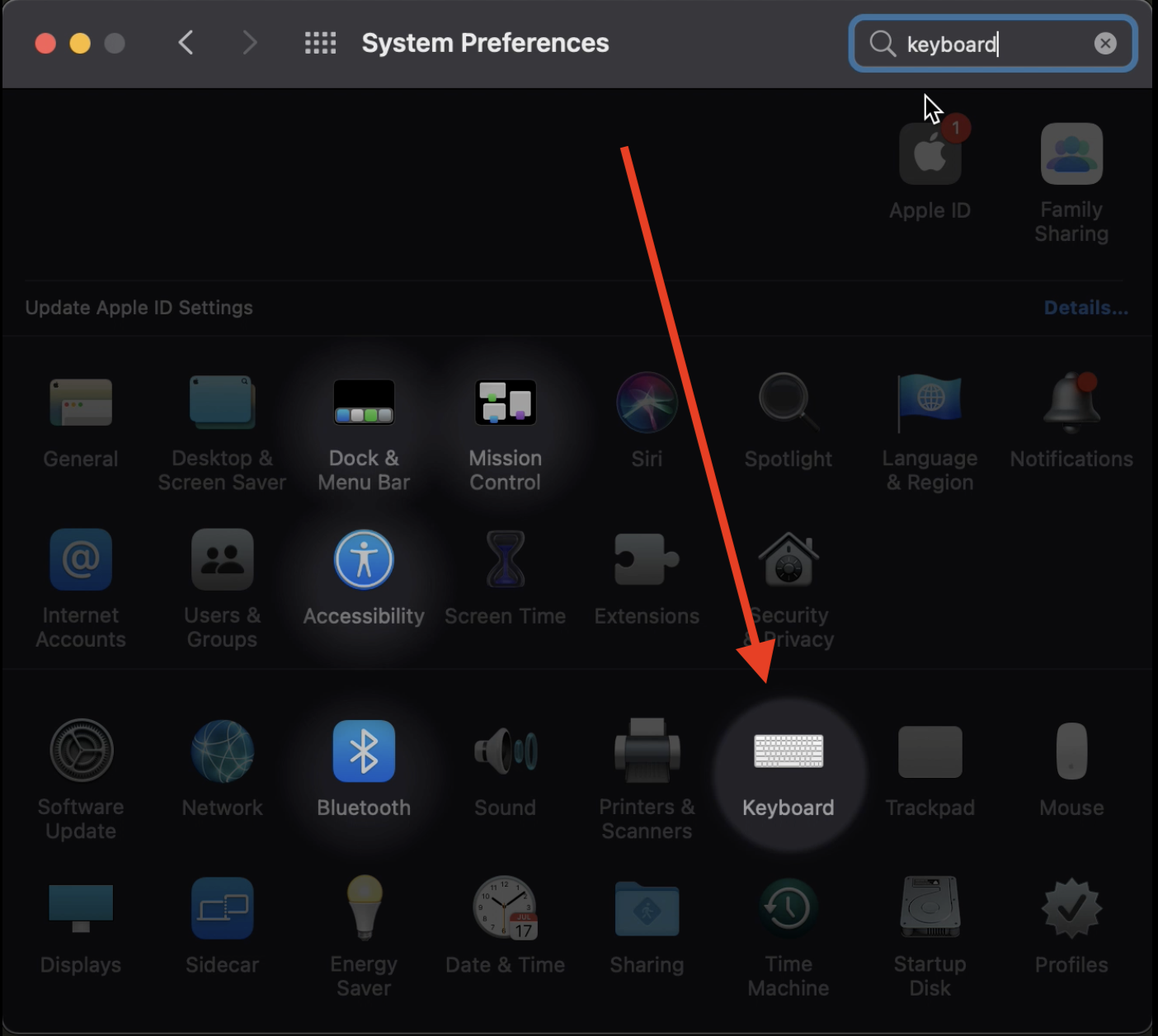
Select the Shortcuts tab. Make sure the box for "Use keyboard navigation to move focus between controls" is checked.
 Additional settings for Safari Browser.
Additional settings for Safari Browser.
Open Safari Preferences:
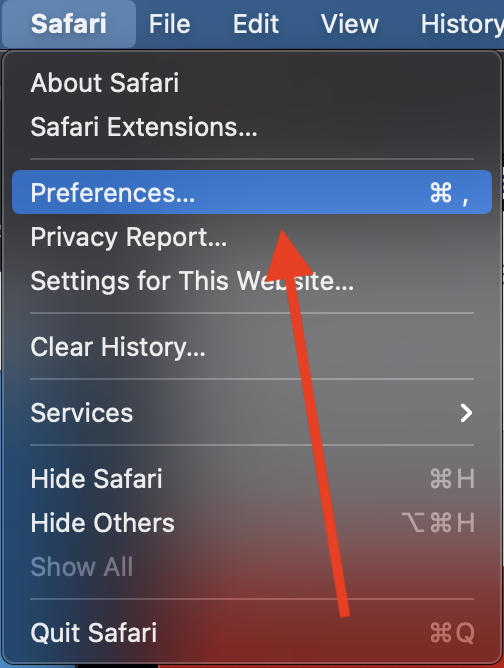
Select the Advanced tab. Make sure the box for "Press Tab to highlight each item on a webpage" is checked.