Portal:Mathematics
The Mathematics Portal
Mathematics is the study of representing and reasoning about abstract objects (such as numbers, points, spaces, sets, structures, and games). Mathematics is used throughout the world as an essential tool in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics, the branch of mathematics concerned with application of mathematical knowledge to other fields, inspires and makes use of new mathematical discoveries and sometimes leads to the development of entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians also engage in pure mathematics, or mathematics for its own sake, without having any application in mind. There is no clear line separating pure and applied mathematics, and practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered. (Full article...)
Featured articles –
Selected image –
Good articles –
Did you know (auto-generated) –

- ... that Hong Wang's latest paper claims to have resolved the Kakeya conjecture, described as "one of the most sought-after open problems in geometric measure theory", in three dimensions?
- ... that the first volume of Felix Klein's books on the history of mathematics does not mention the three women who originally transcribed his lectures?
- ... that Ewa Ligocka cooked another mathematician's goose?
- ... that people in Madagascar perform algebra on tree seeds in order to tell the future?
- ... that in 1940 Xu Ruiyun became the first Chinese woman to receive a PhD in mathematics?
- ... that the discovery of Descartes' theorem in geometry came from a too-difficult mathematics problem posed to a princess?
- ... that The Math Myth advocates for American high schools to stop requiring advanced algebra?
- ... that Carmel Naughton, having been told that girls were "stupid and couldn't do maths", sponsored a STEM scholarship fund?
More did you know –

- ...that every natural number can be written as the sum of four squares?
- ...that the largest known prime number is nearly 41 million digits long?
- ...that the set of rational numbers is equal in size to the set of integers; that is, they can be put in one-to-one correspondence?
- ...that there are precisely six convex regular polytopes in four dimensions? These are analogs of the five Platonic solids known to the ancient Greeks.
- ...that it is unknown whether π and e are algebraically independent?
- ...that a nonconvex polygon with three convex vertices is called a pseudotriangle?
- ...that it is possible for a three-dimensional figure to have a finite volume but infinite surface area, such as Gabriel's Horn?
Selected article –
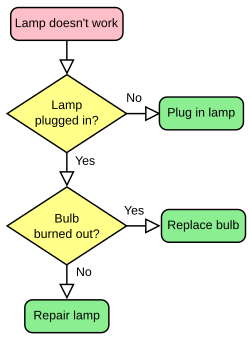 |
| Flowcharts are often used to represent algorithms Image credit: User:Booyabazooka |
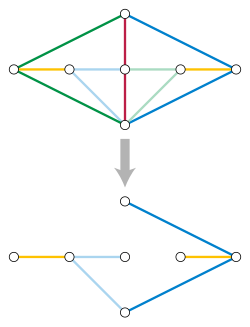
An algorithm is a procedure (a finite set of well-defined instructions) for accomplishing some task which, given an initial state, will terminate in a defined end-state. The computational complexity and efficient implementation of the algorithm are important in computing, and this depends on suitable data structures.
Informally, the concept of an algorithm is often illustrated by the example of a recipe, although many algorithms are much more complex; algorithms often have steps that repeat (iterate) or require decisions (such as logic or comparison). Algorithms can be composed to create more complex algorithms.
The concept of an algorithm originated as a means of recording procedures for solving mathematical problems such as finding the common divisor of two numbers or multiplying two numbers. The concept was formalized in 1936 through Alan Turing's Turing machines and Alonzo Church's lambda calculus, which in turn formed the foundation of computer science.
Most algorithms can be directly implemented by computer programs; any other algorithms can at least in theory be simulated by computer programs. In many programming languages, algorithms are implemented as functions or procedures. (Full article...)
| View all selected articles |
Subcategories

Algebra | Arithmetic | Analysis | Complex analysis | Applied mathematics | Calculus | Category theory | Chaos theory | Combinatorics | Dynamical systems | Fractals | Game theory | Geometry | Algebraic geometry | Graph theory | Group theory | Linear algebra | Mathematical logic | Model theory | Multi-dimensional geometry | Number theory | Numerical analysis | Optimization | Order theory | Probability and statistics | Set theory | Statistics | Topology | Algebraic topology | Trigonometry | Linear programming
Mathematics | History of mathematics | Mathematicians | Awards | Education | Literature | Notation | Organizations | Theorems | Proofs | Unsolved problems
Topics in mathematics
Index of mathematics articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Related portals
WikiProjects
![]() The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
In other Wikimedia projects
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus








.jpg/250px-Beijing_Ancient_Observatory_20090715-19_(cropped).jpg)






.jpg/250px-Leonhard_Euler_-_Jakob_Emanuel_Handmann_(Kunstmuseum_Basel).jpg)